Metals play a crucial role in our daily lives, from powering electronic devices to constructing buildings and vehicles. One of their most important properties is their ability to conduct electricity and heat efficiently. But why are metals good conductors? This article delves into the scientific principles behind metal conductivity, explaining how their unique atomic structure and electron behavior contribute to this essential characteristic.
Understanding Electrical Conductivity in Metals
Electrical conductivity refers to a material’s ability to allow the flow of electric current. In simple terms, it measures how easily electrons can move through a substance. Metals are known for their high electrical conductivity, making them ideal for wiring, circuits, and electronic components. But what exactly makes them so efficient?
The Role of Free Electrons
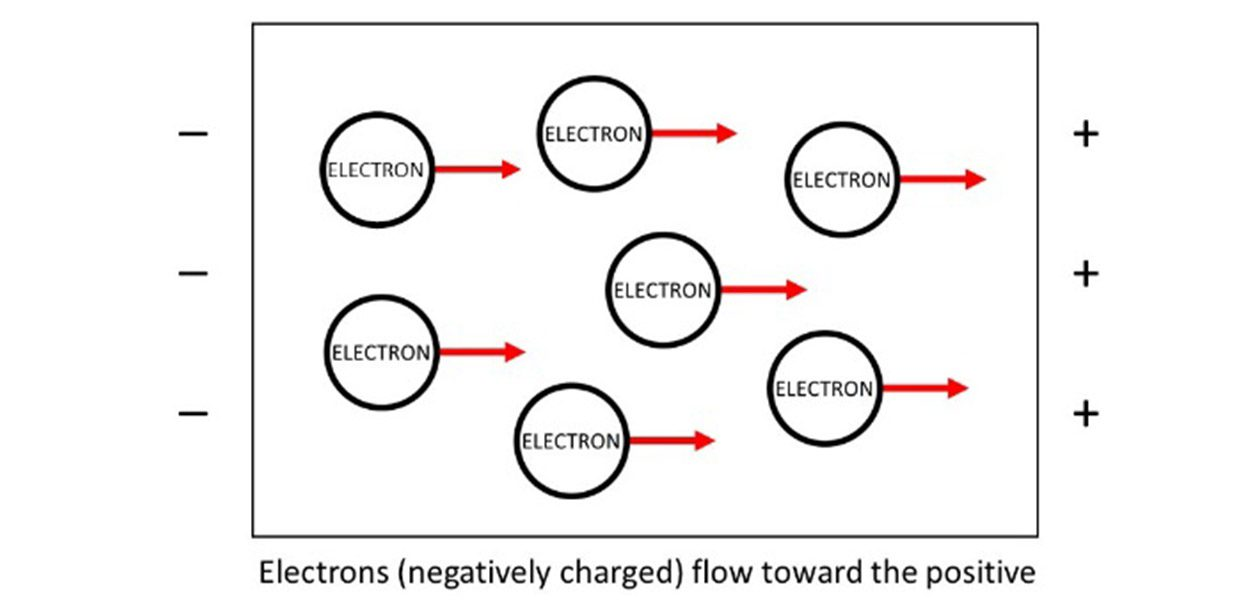
The primary reason why metals are good conductors lies in their atomic structure. Unlike nonmetals, metals have a unique arrangement of atoms where electrons in the outermost energy levels are loosely bound. These valence electrons can move freely within the metal lattice, creating what is known as an electron sea model.
This means that when a voltage is applied, these free-moving electrons flow easily, allowing electricity to pass through the metal with minimal resistance. In contrast, nonmetals have tightly bound electrons that do not move freely, making them poor conductors.
Low Electrical Resistance
Resistance opposes the flow of electric current, and metals typically have low electrical resistance. The free electrons in metals encounter very few obstacles when moving through the material, which enhances their conductivity.
Additionally, factors like purity, temperature, and the presence of impurities can influence the resistance of a metal. For example, copper and silver, two of the best electrical conductors, have minimal impurities and a well-organized atomic structure, which reduces resistance and enhances conductivity.

Why Are Metals Good Conductors of Heat?
Just as metals are excellent conductors of electricity, they are also highly efficient at transferring heat. This property makes them essential for applications such as cookware, radiators, and heat exchangers.
The Mechanism of Heat Transfer in Metals
Heat transfer in metals occurs mainly through conduction, which involves the movement of thermal energy from one part of the material to another. The same free electrons that facilitate electrical conductivity also play a key role in thermal conductivity.
When one part of a metal is heated, the free electrons absorb energy and move rapidly, colliding with other electrons and atoms in the lattice. This process transfers thermal energy throughout the metal, allowing heat to distribute quickly and efficiently.
High Thermal Conductivity of Metals
Certain metals, such as copper, silver, and aluminum, exhibit high thermal conductivity, making them ideal for applications requiring efficient heat transfer. For instance, copper is widely used in heat sinks and cooking utensils because it can quickly distribute heat, ensuring even cooking and preventing hot spots.
Conversely, materials with low thermal conductivity, such as wood and rubber, do not have free electrons to carry heat efficiently, making them excellent insulators rather than conductors.
Factors That Influence Metal Conductivity
Although metals are generally good conductors, several factors can affect their electrical and thermal conductivity:
1. Type of Metal
Not all metals conduct electricity and heat with the same efficiency. Some of the best conductors include:
- Silver – The best electrical conductor but expensive.
- Copper – A close second, widely used in electrical wiring.
- Gold – A good conductor that resists corrosion, making it ideal for high-end electronics.
- Aluminum – Lightweight and cost-effective, often used in power lines.
2. Temperature
Temperature plays a significant role in conductivity.
- Electrical Conductivity: Most metals increase in resistance as temperature rises, meaning their conductivity decreases at higher temperatures. This happens because atomic vibrations interfere with the movement of free electrons.
- Thermal Conductivity: While metals generally remain good heat conductors at high temperatures, excessive heat can cause structural changes, affecting their efficiency.
3. Impurities and Alloying
Pure metals typically conduct electricity and heat better than alloys. However, some applications require the addition of other elements to enhance strength, durability, or resistance to corrosion.
- Pure Copper vs. Copper Alloys: While pure copper is highly conductive, adding other metals (such as zinc in brass) reduces its conductivity.
- Stainless Steel: An alloy of iron, chromium, and nickel, which has lower electrical and thermal conductivity compared to pure metals like silver or copper.
4. Structural Defects
Metals with fewer defects in their crystalline structure tend to conduct electricity and heat more efficiently. Manufacturing processes such as annealing (controlled heating and cooling) can improve conductivity by reducing defects.
Applications of Metal Conductivity
Understanding why metals are good conductors helps us appreciate their widespread use in various industries. Here are some key applications:
1. Electrical Wiring and Power Transmission
Metals like copper and aluminum are used extensively in electrical wiring, power grids, and electronic circuits due to their superior conductivity and durability.
2. Heat Exchangers and Cooling Systems
Metals like aluminum and copper are widely used in radiators, HVAC systems, and heat exchangers because they quickly transfer heat, preventing overheating in machinery and devices.
3. Cookware and Kitchen Utensils
Stainless steel and copper cookware are popular choices because they distribute heat evenly, ensuring efficient cooking.
4. Electronics and Microchips
Gold and silver are commonly used in high-end electronics, including smartphones and computers, due to their excellent conductivity and resistance to oxidation.
5. Aerospace and Automotive Engineering
Aluminum and titanium, known for their lightweight and conductive properties, are used in spacecraft, aircraft, and automobiles for both electrical and heat management systems.
Conclusion: Why Are Metals Good Conductors?
Metals are excellent conductors of both electricity and heat due to their free-moving electrons, low resistance, and unique atomic structure. These properties make them indispensable in various industries, from electrical engineering to cookware and aerospace technology.
However, not all metals conduct electricity and heat equally. Factors such as metal type, temperature, impurities, and structural composition influence their efficiency. Silver, copper, and aluminum stand out as some of the best conductors, while alloys and certain metals with impurities exhibit lower conductivity.
In summary, why are metals good conductors? The answer lies in their fundamental atomic structure and the behavior of their electrons. This fascinating property continues to shape modern technology and innovation, proving the immense value of metals in our everyday lives.

